Robot Operating System (ROS) & Application
What is Robot Operating System ?
Robot Operating System or simply ROS is a framework which is used by hundreds of Companies and techies of various fields all across the globe in the field of Robotics and Automation. It provides a painless entry point for nonprofessionals in the field of programming Robots.
Although ROS is not an operating system, it provides services designed for a heterogeneous computer cluster such as hardware abstraction, low-level device control, implementation of commonly used functionality, message-passing between processes, and package management. Here is a presentation on the same.
ROS is the culmination of the underlying infrastructure for robotic control, a robust set of tools, a collection of capabilities than can be mixed and matched and a broad community ecosystem of developers working on specific topic areas
ROS is not an operating system but a meta operating system meaning, that it assumes there is an underlying operating system that will assist it in carrying out its tasks.
ROS and underlying operating system
OS depends on the underlying Operating System. ROS demands a lot of functionality from the operating system. On top of that ROS must be freely available to a large population, otherwise, a large population may not be able to access it. Much of the popularity of ROS is due to its open nature and easy availability to the mass population. It also needs an operating system that is open source so the operating system and ROS can be modified as per the requirements of application.

Proprietary Operating Systems such as Windows 10 and Mac OS X may put certain limitations on how we can use them. This may lead to rigidity in the development process, which will not be ideal for an industry-standard like ROS. Hence, most people prefer to run ROS on Linux particularly Debian and Ubuntu since ROS has very good support with Debian based operating systems especially Ubuntu. That doesn’t mean that ROS can’t be run with Mac OS X or Windows 10 for that matter. But the support is limited and people may find themselves in a tough situation with little help from the community.
There is close proximity between ROS and OS, so much so that it becomes almost necessary to know more about the operating system in order to work with ROS. Using Linux as a newbie can be a challenge, One is bound to run in issues with Linux especially when working with ROS, and a good knowledge of Linux will be helpful to avert/fix these issues.
- A Meta Operating system has a huge amount of functionality, so much that it cannot be classified as a framework or a cluster of libraries but not so much that it can be categorized as an operating system either. It provides functionalities of both Operating Systems as well as frameworks but not fully hence, it cannot be classified as either e.g, it does not provide the core functionalities that an operating system is supposed to provide but provides APIs.
- RViz is a 3D Visualization tool for ROS. It is one of the most popular tools for visualization. It takes in a topic as input and visualizes that based on the message type being published. It lets us see the environment from the perspective of the robot.
Core ROS Components
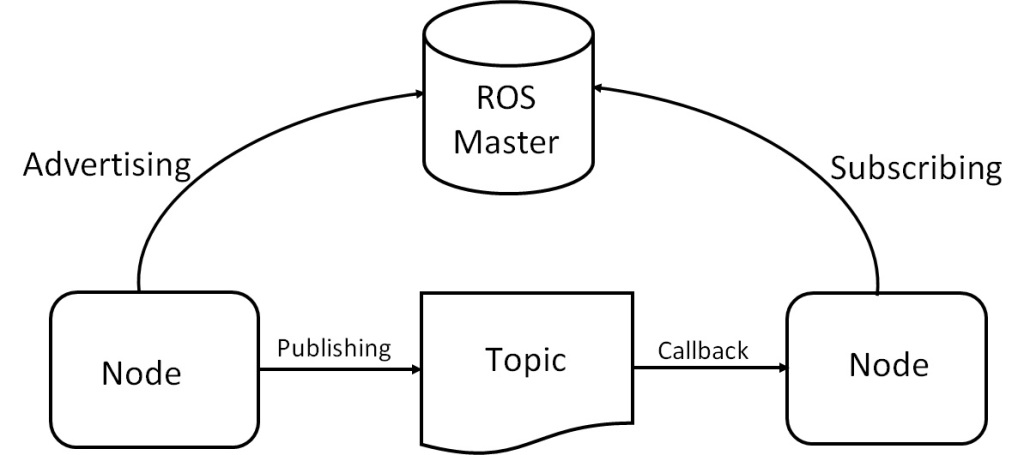
At its core, ROS is an anonymous publish/subscribe message-passing middleware. Some modules will publish a set of topics while others subscribe to that topic. When new data is published, the subscribers can learn about the updates and can act on them. Communication is implemented using a message-passing approach that forces developers to focus on clean interface logic. It is described in the message interface definition language (IDL). ROS supports the recording and playback of messages. Messages can be recorded to a file and then played back to republish the data at any time.It allows for repeatability and facilitates regression testing.
Support for remote procedure calls via services
• While asynchronous communications via pub/sub is great, sometimes you need lock-step
synchronous behaviors
• Distributed parameter system
• Tasks can share configuration information via a global key-value store
• Provides a centralized point for changing configuration settings and the ability to change settings in
distributed modules
• Robot-specific features like a geometry library, mapping and navigation
functions, diagnostics and much more
• Extensive diagnostics capabilities
ROS Concepts
ROS has three levels of concepts:
• Filesystem level
• Computation level
• Community level
The filesystem level encompasses resources you’ll likely encounter on disk
• Packages
• Meta packages
• Package manifests
• Repositories
ROS computation graph level concepts include:
• Nodes Topics
• Master Services
• Parameter server Bags (places to store collected data)
• Messages
The ROS community-level concepts facilitate the exchange of software and knowledge between members of the community
• Distributions
• Repositories
• The ROS Wiki
• Bug ticket system
ROS Features:
- Code reuse (exec. nodes, grouped in packages)
- Distributed, modular design (scalable)
- Language independent (C++, Python, Java, …)
- ROS-agnostic libraries (code is ROS independent)
- Easy testing (ready-to-use)
- Vibrant community & collaborative environment
Robot Specific Features
- Standard Message Definitions for Robots
- Robot Geometry Library • Robot Description Language
- Preemptable Remote Procedure Calls
- Diagnostics • Pose Estimation
- Localization
- Mapping
- Navigation
ROS was meant for particular use cases. Since then, a lot has changed, We have seen a resurgence in Artificial Intelligence research and increase in the number of use cases. Robotics is becoming more popular among the masses and even though ROS copes up with these challenges very well(even though it wasn’t made to), it requires a great number of hacks.
History and Legacy

It started in 2007 as an outgrowth of the Stanford AI Robot (STAIR) and
Personal Robots (PR) programs from Stanford University in Stanford, CA.
The project was sponsored by an local robotics incubator named Willow Garage. Willow Garage produced a robot known as the PR2. The purchasers of the PR2 became a loose federation of developers, each contributing their code back to the greater community.
Licensed under the permissive BSD open-source license. However, some modules have licenses like ASLv2, GPLv2, MIT, etc. Latest release is “Lunar Loggerhead” in May of 2017. ROS is supported by the Open Source Robotics Foundation https://www.osrfoundation.org/
Integration with Libraries
ROS provides seamless integration of famous libraries and popular open-source projects.




We hope you enjoyed….
Thank you for reading!!!
made with love . . . . . . . .
– by AIML Roll No. 1,2,3,4,42
(From TCET)